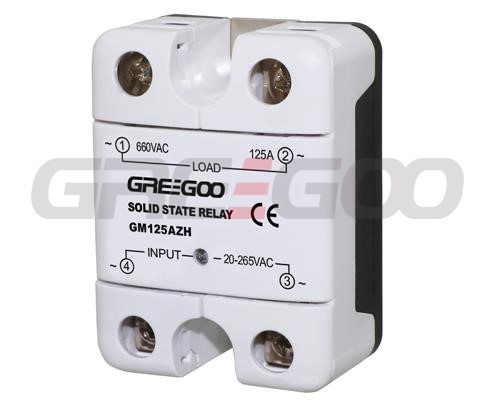
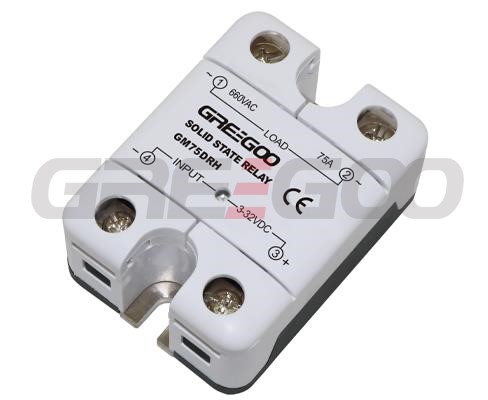
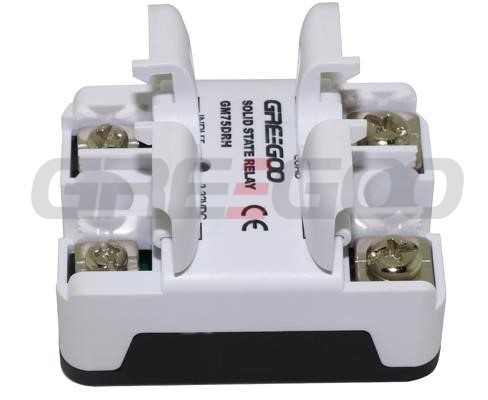
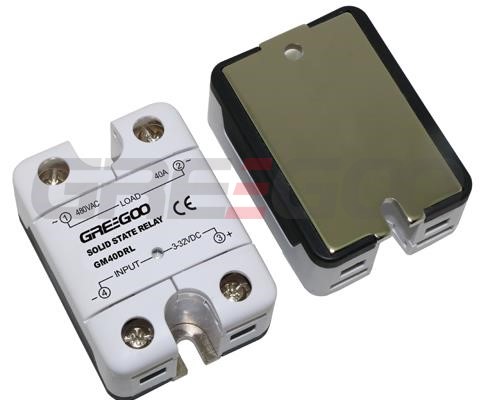
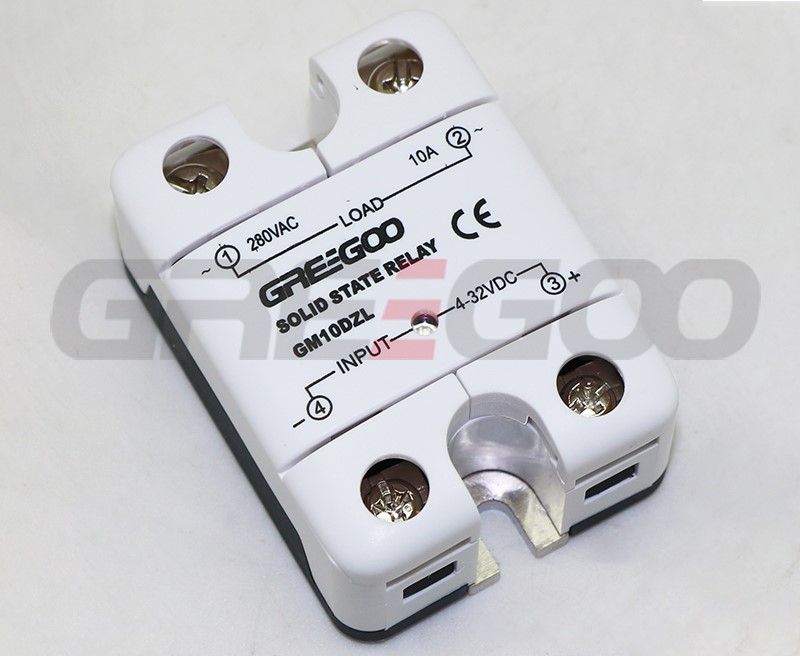
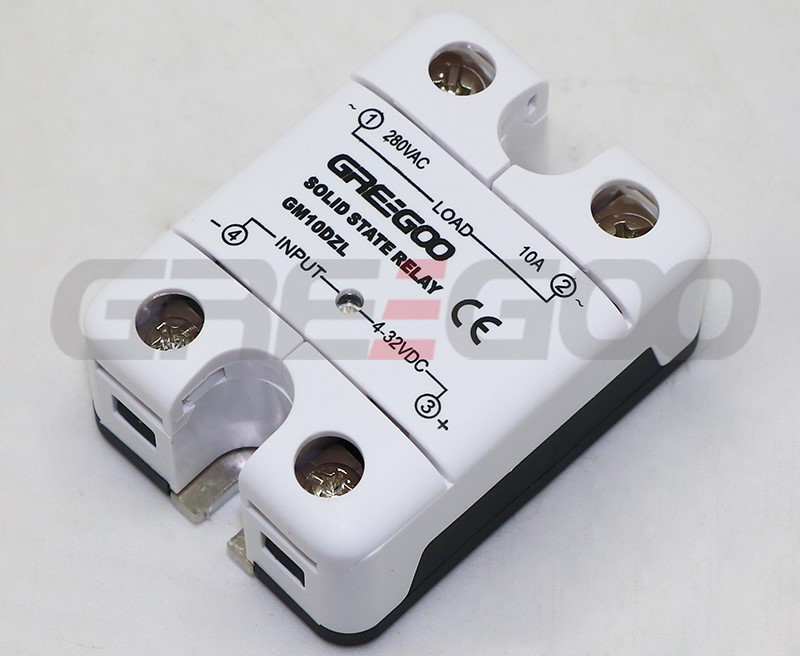
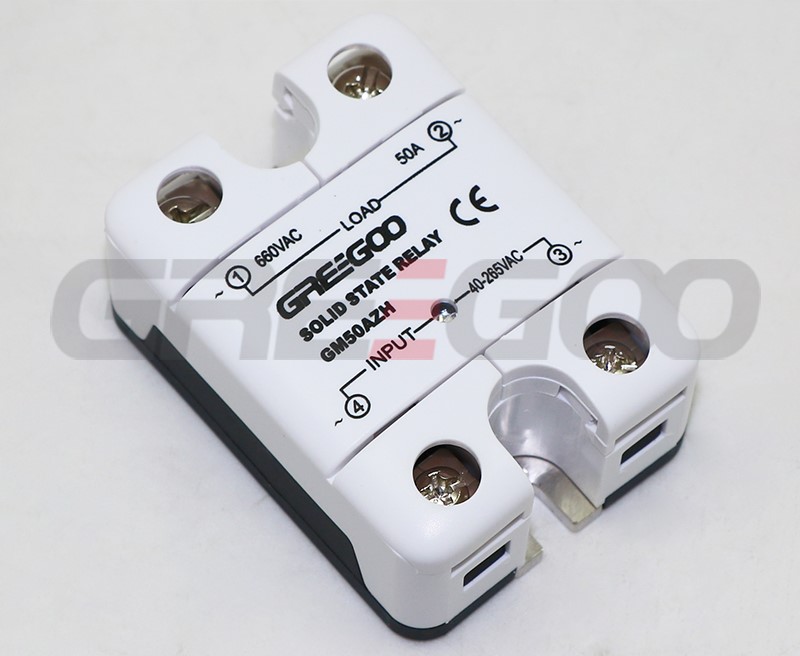
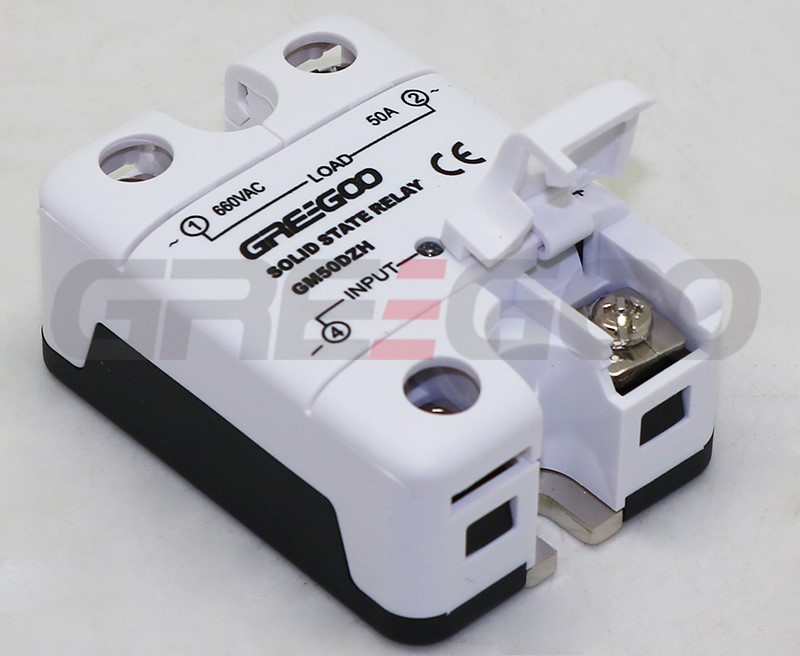
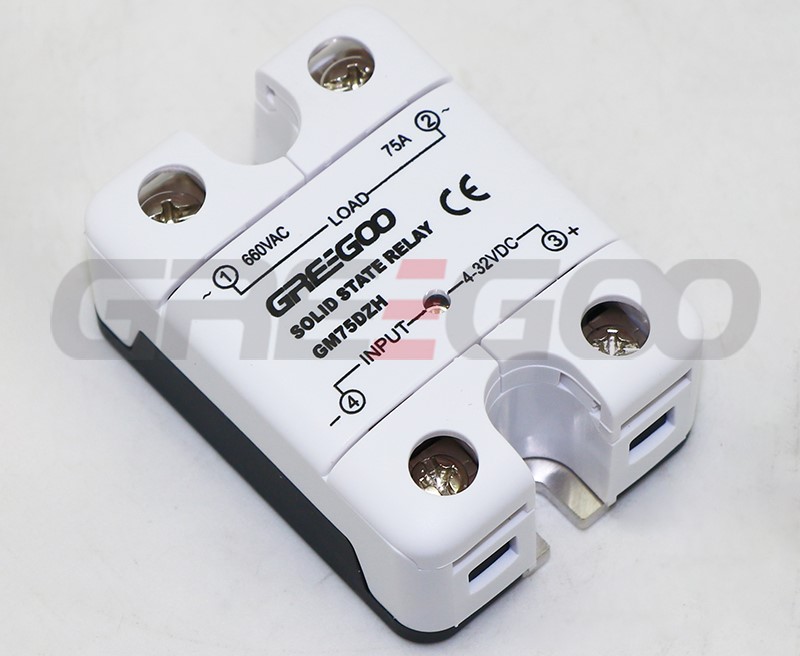
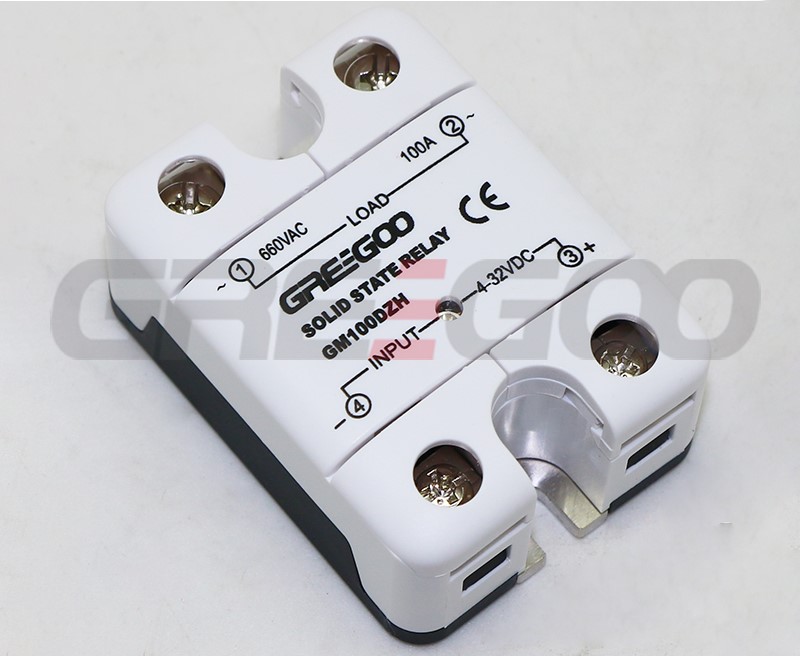
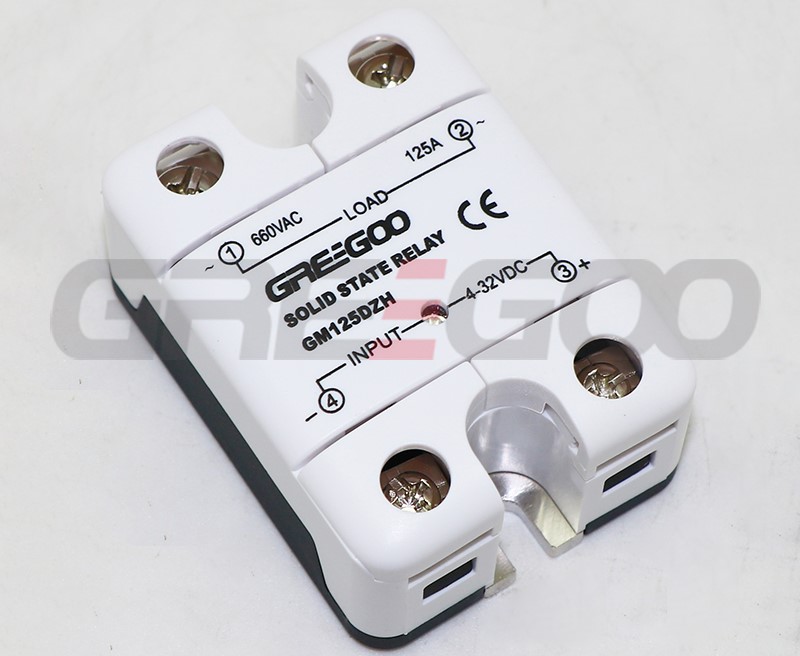
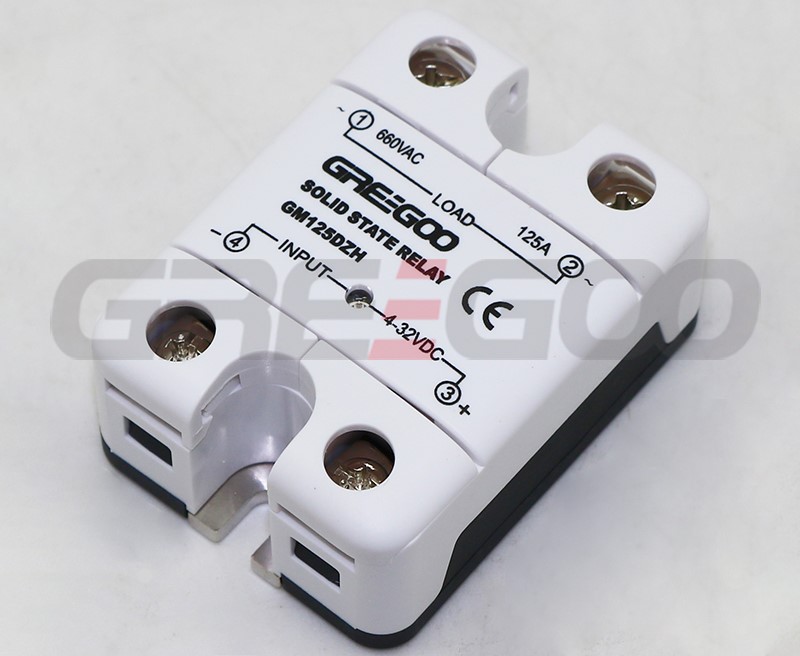
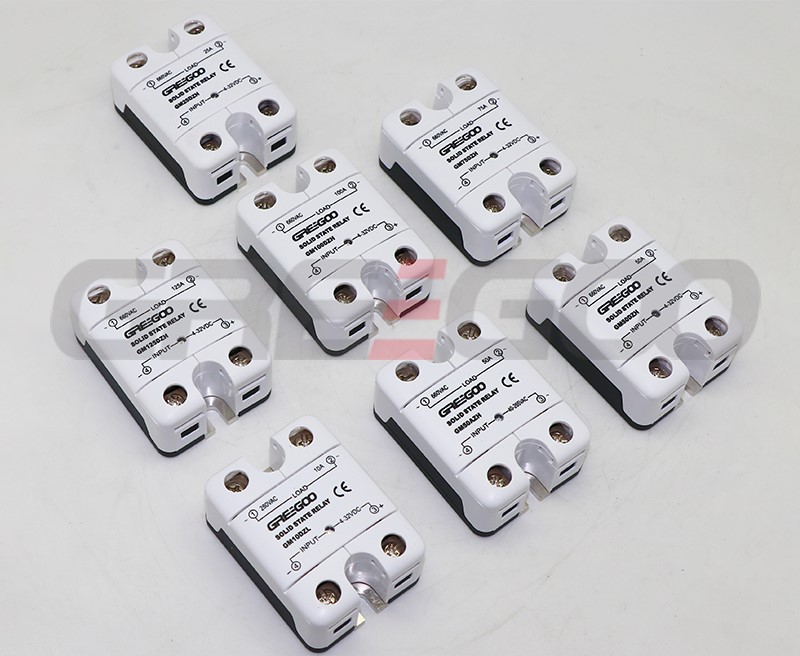
Integrated IP20 touch-safe removable covers Solid State Relays
Home Products Solid State Relays (AC Switching)Single Phase Solid State RelaysIntegrated IP20 touch-safe removable covers Solid State Relays
Integrated IP20 touch-safe removable covers Solid State Relays
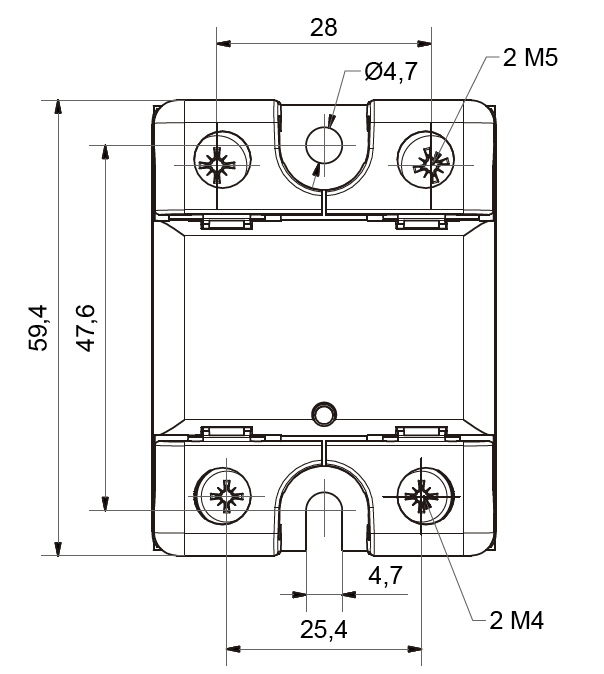
GM Series panel mount single phase AC output Solid State Relays are designed to be used in almost any application, offering very long life expectancy and are easy to install, easy to use, robust and multipurpose.
››Output current of 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 125 Amps
››Output voltage of 24-280 Vac and 48-660 Vac
››Control voltage of 4-32 Vdc, 18-36 Vac/dc, 40-265 Vac and 90-260 Vac
››Zero cross or instantaneous (resistive or inductive loads)
››Integrated IP20 touch-safe removable covers
››Built-in overvoltage protection (only Zero Cross)
››LED input status indicator
Standard type
| Model No. | Output Current | Output Voltage | Input Voltage | Switching | Output protection |
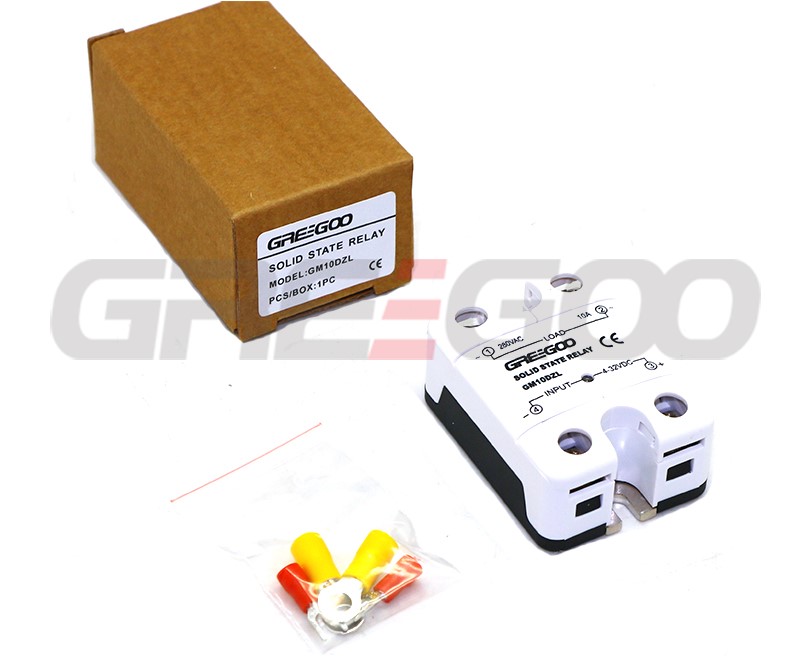
| GM10DZL | 10A | 24-280 VAC | 4-32 VDC | Zero Cross | TVS |
| GM10AZL | 10A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM25DZL | 25A | 24-280 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM25CZL | 25A | 18-36V AC/DC | |||
| GM25AZL | 25A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM25DZH | 25A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM25AZH | 25A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM50DZH | 50A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM50CZH | 50A | 18-36V AC/DC | |||
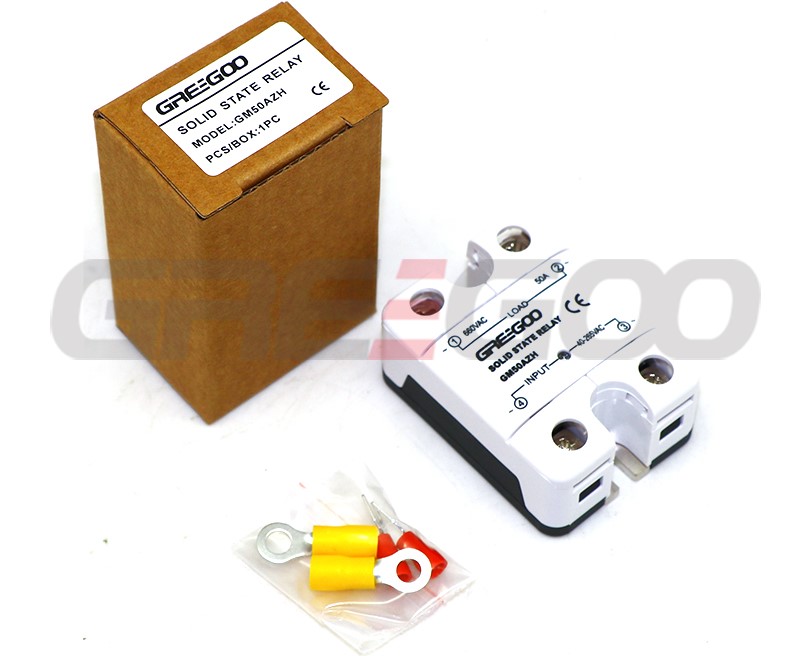
| GM50AZH | 50A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM75DZH | 75A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM75AZH | 75A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM100DZH | 100A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM100AZH | 100A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM125DZH | 125A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM125AZH | 125A | 40-265 VAC | |||
| GM25DRL | 25A | 24-280 VAC | 4-32 VDC | Random | RC Snubber |
| GM25ARL | 25A | 90-260 VAC | |||
| GM50DRH | 50A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC | ||
| GM50ARH | 50A | 90-260 VAC | |||
| GM75DRH | 75A | 48-660 VAC | 4-32 VDC |
The main differences between Solid State Relays (SSR) and Electromechanical Relays (EMR) lie in their structure and performance. SSRs have no mechanical contacts and use semiconductor devices for switching, offering longer lifespan, faster switching speeds, and noiseless operation, making them suitable for high-frequency operations and harsh environments. EMRs rely on electromagnetic coils to drive mechanical contacts, resulting in slower switching speeds, shorter lifespan, and noise during operation, and they are more sensitive to vibration and shock. SSRs consume less power and are ideal for applications requiring frequent switching, such as heating and motor control, while EMRs are suitable for general switching applications, especially where electrical isolation is needed.
SSRs have no mechanical parts, reducing the risk of arcing, making them more durable and reliable in high-frequency switching applications. Solid state relays can significantly decrease both downtime and maintenance costs.
A margin should be left when selecting the voltage and current of the solid state relay. For resistive load: the current is selected according to 2.5~4 times the load current, and the voltage is selected according to 2~2.5 times the load power. Inductive load: current is selected according to 3-7 times load current, voltage is selected according to 2.5-3 times load voltage.
Thyristor modules require a dedicated trigger circuit to provide precise trigger pulses, suitable for applications needing precise control. Solid-state relays are triggered via optocouplers, featuring built-in electrical isolation, and are easy to install, making them suitable for applications with lower switching frequencies. The anti-interference capability of thyristor modules depends on the design of the trigger circuit, while solid-state relays have relatively strong anti-interference due to optocoupler isolation, though electromagnetic interference should still be considered.
Need more information?
Contact us to request pricing, availability and customization options.

Solid state relay with heatsink integrated
17.5mm solid state contactor, integrated heatsink with din rail clamps, 15A, 25A, 40A and 60A.
View More
Compact FASTON terminals ac switching solid state relay
1-Phase, 15A and 25A, 230VAC, FASTON terminals connect
View More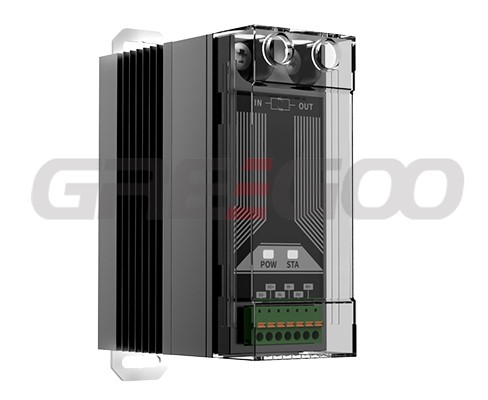
Solid state relay with diagnostic
Status output built in solid state relay
View More




























