Differences Between Vacuum Relay, SPST-NC, STST-NO, SPDT, and DPDT Switches
The differences between vacuum relay, SPST-NC, SPST-NO, SPDT, and DPDT mainly lie in their structure and function:
-
Vacuum Relay:
- Structure: Operates within a vacuum chamber to prevent arc formation.
- Function: Suitable for high-voltage switching, reduces contact wear, responds quickly, and is commonly used in high-voltage circuits requiring fast switching.
-
SPST-NC (Single Pole Single Throw Normally Closed):
- Structure: Has one input and one output, and the circuit is closed by default.
- Function: Used to keep the circuit closed when not energized and open the circuit when energized.
-
SPST-NO (Single Pole Single Throw Normally Open):
- Structure: Has one input and one output, and the circuit is open by default.
- Function: Used to keep the circuit open when not energized and close the circuit when energized.
-
SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw):
- Structure: Has one input and two outputs.
- Function: Can switch between two outputs, commonly used in applications requiring switching between two circuits.
-
DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw):
- Structure: Has two inputs and two outputs.
- Function: Can switch two independent circuits simultaneously, suitable for applications requiring simultaneous control of two circuits.
These types of relays and switches have different uses in circuit design, and the choice depends on specific application requirements.

Dual Thyristor Module vs Dual Diode Module vs Thyristor Diode Module, what's their difference?
Difference between dual thyristor module, dual diode module and thyristor diode combined module
Read More
Mini Puck Solid-State Relay: A Compact and Reliable High-Efficiency Switching Solution
The GF1 solid state relay uses back-to-back thyristors for switching, which are more durable than traditional triacs.
Read More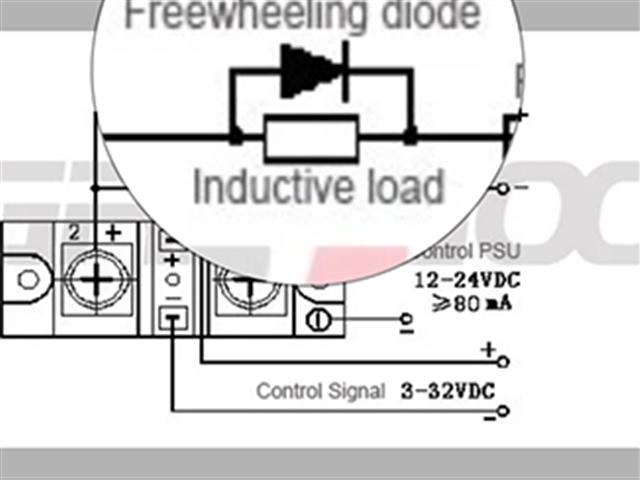
The Critical Role and Application Analysis of Freewheeling Diodes in Solid-State Relay
The freewheeling diode plays a critical protective role in solid-state relays, especially when controlling inductive loads. It effectively suppresses back electromotive force, protects the power components of the solid-state relay, reduces electromagnetic interference, and enhances the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Read More
Guide to Heatsink Calculation and Selection
A heatsink is a device used for heat dissipation, commonly found in electronic devices to help dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
Read More













