Guide to Heatsink Calculation and Selection
A heatsink is a device used for heat dissipation, commonly found in electronic devices to help dissipate heat and prevent overheating. When calculating the performance of a heatsink or selecting an appropriate one, the following aspects are typically considered:


4. Heatsink Material and Design
The material and design of the heatsink also affect its performance:
- Material: Common materials include aluminum and copper. Copper has better thermal conductivity, but aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective.
- Design: The surface area, number of fins, and shape of the heatsink all influence its heat dissipation performance.
5. Practical Considerations
In practical applications, the following factors should also be considered:
- Air Cooling or Liquid Cooling: Air-cooled heatsinks rely on airflow, while liquid-cooled heatsinks use circulating liquid for heat dissipation.
- Installation Method: Ensure good contact between the heatsink and the heat source. Thermal paste or thermal pads can be used to improve heat conduction efficiency.

Excitation technology rectifier components for 30-1350MW steam turbine generators
No maintenance of slip rings and carbon brushes, high reliability; There is no pollution of the motor coil caused by carbon powder and copper powder, and the insulation life is long; No friction sparks, suitable for operation in harsh environments.
Read More
Comparison of Solid State Relays and AC Contactors in Terms of Instantaneous Current Withstand Capability
Therefore, in applications that require handling high instantaneous currents, AC contactors are usually more suitable than solid state relays.
Read More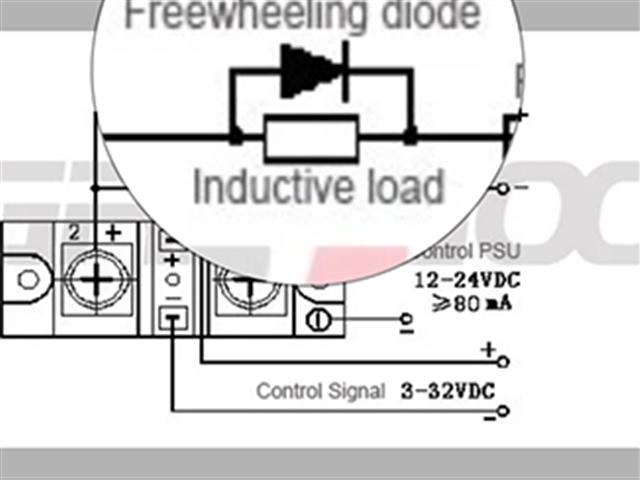
The Critical Role and Application Analysis of Freewheeling Diodes in Solid-State Relay
The freewheeling diode plays a critical protective role in solid-state relays, especially when controlling inductive loads. It effectively suppresses back electromotive force, protects the power components of the solid-state relay, reduces electromagnetic interference, and enhances the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Read More
1.14 kV Vacuum Contactors: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency in Low-Voltage Switching for Industry Application.
1.14 kV vacuum contactor is a specialized type of contactor that uses vacuum interrupters to switch electrical circuits at high voltages. Vacuum contactors are widely used in various industrial applications due to their reliability, safety, and efficiency.
Read More














