Excitation technology rectifier components for 30-1350MW steam turbine generators
At present, our main products are the series of brushless excitation and rectifier components for 30-1350MW steam turbine generators. Brushless excitation technology is widely used in generators and motors, especially large generators. Because the rectifier assembly is fixed with the exciter rotor of the unit and rotates synchronously, eliminating the need for commutators, slip rings and carbon brushes, it has the incomparable advantages of brush excitation.
Your benefits:
- No maintenance of slip rings and carbon brushes, high reliability;
- There is no pollution of the motor coil caused by carbon powder and copper powder, and the insulation life is long;
- No friction sparks, suitable for operation in harsh environments.
The rotating excitation rectifier assembly is composed of main components and parts such as rectifier, capacitor, fuse, radiator and conductive parts, insulating parts and fasteners. It has the advantages of small size, strong function and high technical content. It is a functional component integrating heat, power and electricity. Based on the special structure of the rotating excitation rectifier components and the harsh operating environment, the company has established a complete quality management system. There are strict management and inspections from material selection, component selection, outsourcing parts inspection to processing technology, installation technology and testing. Thereby ensuring that the company's products fully meet the technical requirements of customers, long-term and reliable operation.
Our case:
|
Application |
Rated Current |
Rated Voltage |
Forward Voltage |
Centrifugal Acceleration |
Tangential Acceleration |
TVJM |
|
Rectifier Assemblies for Rotating Exciter in 1350MW Nuclear Generator |
800 |
2000 |
1.20 ±0.025 |
6000 |
±500 |
175 |
|
Rectifier Assemblies for Rotating Exciter in 1000MW Steam Turbine Generator |
1000 |
2600 |
1.55 |
6000 |
±600 |
175 |
|
Rectifier Assemblies for Rotating Exciter in 600MW Steam Turbine Generator |
800 |
2000 |
1.20 ±0.025 |
6000 |
±500 |
175 |
|
Rotating excitation assembly of 300MW turbine generator |
400 |
2000 |
1.20~1.25 ±0.025 |
6000 |
±500 |
175 |
|
Rectifier Assemblies for Rotating Exciter in 50~150MW Air-cooing Steam Turbine Generator |
400 |
2000 |
1.20~1.25 ±0.025 |
6000 |
±500 |
175 |
|
Rectifier Assemblies for Rotating Exciter in 30MW Steam Turbine Generator |
400 |
2000 |
1.20~1.25 ±0.025 |
6000 |
±500 |
175 |

DC solid state relay and DC contactor, which one is better?
DC Solid State Relays (DC SSR) and DC contactors are both switching devices used to control circuits, but they have significant differences in working principles, performance and application.
Read More
What are the main differences between MOVs and Spark Gaps in SPDs?
An effective surge protection strategy often combines the use of both MOVs and spark gaps, along with other protective devices, to provide comprehensive protection against different levels of power surges.
Read More
How to order a suitable high voltage relay?
A high voltage relay that includes any relay capable of handling high voltage applications, typically in the kilovolt range and above. These relays can be vacuum relays, but they might also be gas-filled or solid-state relays, depending on the specific application requirements.
Read More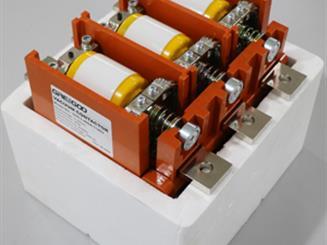
What is the difference between the magnetic latching type and electrical holding type vacuum contactor?
Vacuum contactors can be classified into two main types based on their mechanism for holding the contacts closed: magnetic latching type and electrical holding type.
Read More













