Advanced Low-Power Short-Range Millimeter-Wave Radar Module: Features and Applications
The low-power, short-range millimeter-wave radar module is an advanced sensor technology primarily used for detecting and measuring the distance, speed, and angle of objects. Operating in the 30 GHz to 300 GHz frequency band, millimeter-wave radar offers high resolution and penetration capabilities, making it particularly suitable for precise short-range detection.
Here are some key features and applications of the low-power, short-range millimeter-wave radar module:
Key Features
- Low Power Consumption: Optimized design to reduce energy consumption, suitable for battery-powered devices.
- Short-Range Measurement: Typically used for detection within a few meters to several tens of meters.
- High Resolution: Due to the shorter wavelength of millimeter waves, it can achieve high-precision distance and speed measurements.
- All-Weather Operation: Unaffected by light and weather conditions, it can operate stably in various environments.
- Miniaturization: Modular design, easy to integrate into various devices.
Application Fields
- Automotive Industry: Used for blind spot detection, parking assistance, and adaptive cruise control.
- Industrial Automation: Used for robot navigation, object recognition, and distance measurement.
- Smart Home: Used for intrusion detection, personnel tracking, and indoor positioning.
- Medical Health: Used for monitoring vital signs such as breathing and heartbeat detection.
- Consumer Electronics: Used for gesture recognition in smartphones and tablets.
Technical Principle Millimeter-wave radar detects objects by emitting millimeter-wave signals and receiving the signals reflected back from the target object. By analyzing information such as the time delay and frequency shift of the echo signals, it can calculate the distance, speed, and angle of the target object.
Selection and Integration When selecting a millimeter-wave radar module, the following factors need to be considered:
- Operating Frequency Band: Choose the frequency band suitable for specific applications.
- Detection Range: Select an appropriate detection distance based on application requirements.
- Power Consumption Requirements: Ensure that the module's power consumption meets the device's power design.
- Interface and Protocols: Ensure compatibility of the module with other system components.
In summary, the low-power, short-range millimeter-wave radar module has a broad application prospect in modern technology and is an important means for achieving intelligence and automation.
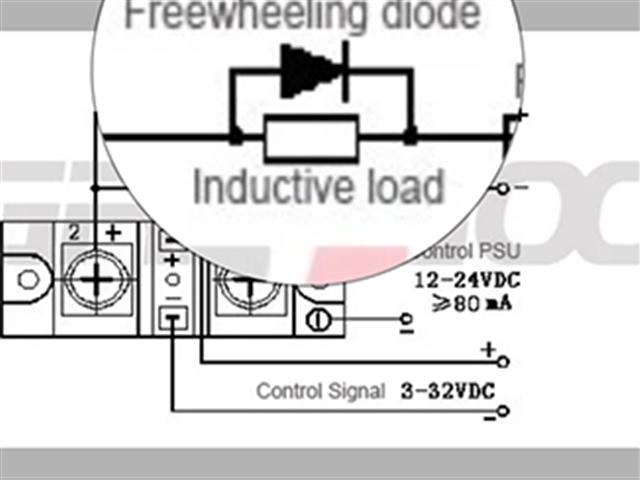
The Critical Role and Application Analysis of Freewheeling Diodes in Solid-State Relay
The freewheeling diode plays a critical protective role in solid-state relays, especially when controlling inductive loads. It effectively suppresses back electromotive force, protects the power components of the solid-state relay, reduces electromagnetic interference, and enhances the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Read More
What is the main difference between 8/20μs and 10/350μs in SPD?
8/20μs: Suitable for protection against fast-rising and short-duration surges, such as lightning strikes and rapid switching events.10/350μs: Suitable for protection against slower-rising and longer-duration surges, often associated with power distribution network switching operations and industrial electrical systems.
Read More
Gas-Filled Relays vs. Vacuum Relays: A Comparison and Application in High Voltage Switching Technology
the difference between gas filled relay and vacuum relay
Read More
𝐃𝐢𝐟𝐟𝐞𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞 𝐁𝐞𝐭𝐰𝐞𝐞𝐧 𝐃𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐓𝐡𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞 𝐃𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐝𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐓𝐡𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫-𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐝𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞
𝐃𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐓𝐡𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞 vs 𝐃𝐮𝐚𝐥 𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐝𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞 vs 𝐓𝐡𝐲𝐫𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫-𝐃𝐢𝐨𝐝𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐥𝐞, what's their difference from function and structure?
Read More













